



Curie temperature, also known as Curie point and magnetic transition point, refers to the temperature at which the magnetic field strength of the magnetic material itself drops to 0. It was discovered by the Curies at the end of the 19th century: when the magnet is heated to a certain temperature, the original magnetism disappears.
In transformers (inductors), if the temperature of the core exceeds the Curie temperature, the inductance will become zero, and most products can recover after a certain period of time after returning to normal temperature. However, for the transformer (inductor) in the working state, if the inductance drops to 0, it will directly fail, causing the transformer (inductor) to burn out.
Therefore, for the design and selection of transformers (inductors), it is necessary to reserve corresponding margins to keep the temperature of the core below the Curie temperature when the transformer (inductor) is working.
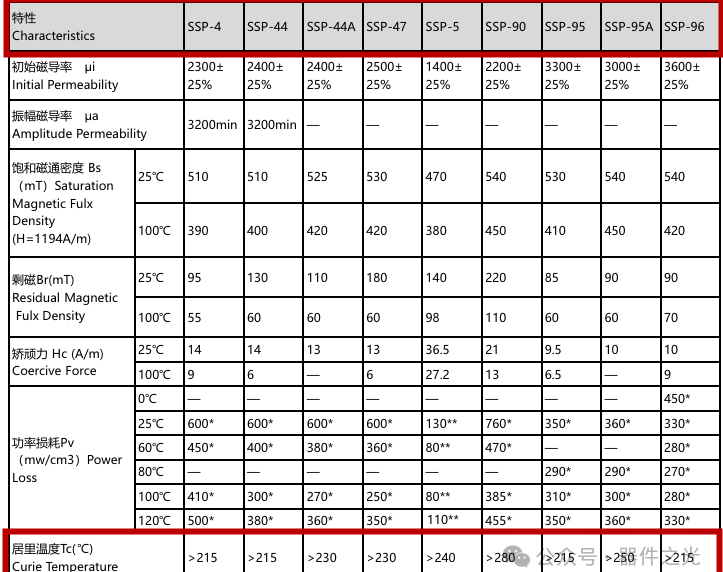
Power manganese-zinc ferrite, Curie temperature above 210 °C. Most transformer (inductor) insulation materials are lower than this temperature, and the core does not normally have such a high temperature when the transformer (inductor) is operating.
High conductivity manganese-zinc ferrite, Curie temperature above 110 °C. Most transformer (inductor) insulation materials are higher than this temperature, and the temperature of the transformer (inductor) after operation can easily exceed this temperature. Therefore, special attention should be paid to the design of high-permeability cores, and the temperature of the cores under working conditions should be below the Curie temperature.
For nickel-zinc ferrite, the Curie temperature is above 100 °C, and like the high-conductivity ferrite, it is necessary to focus on the transformer (inductor) when working, and the temperature of the core cannot exceed the Curie temperature. This is especially important for our commonly used nickel-zinc products, such as I-shaped inductors, rod inductors, and nickel-zinc ring inductors.
Alloy powder core, Curie temperature above 450 °C, relatively high. In this case, we need to pay more attention to the temperature resistance level of the other components of the transformer (inductor).
Scan the code to follow